Assignment 3 (V2)
A. Consider a rectangular piece of metal alloy, four times as wide as
high, consisting of three different metals, each with different
thermal characteristics. For each region of the alloy, there is a
given amount (expressed in terms of a percentage) of each of the three
base metals, that varies up to 20 percent due to random noise. The
top left corner (at the mesh element at index [0,0]) is heated
at 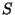 degrees Celsius and the bottom right corner
(index [width - 1,height - 1]) is heated at
degrees Celsius and the bottom right corner
(index [width - 1,height - 1]) is heated at 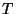 degrees Celsius. The temperature at these points may also randomly
vary over time.
degrees Celsius. The temperature at these points may also randomly
vary over time.
Your program calculates the final temperature for each region on the
piece of alloy. The new temperature for a given region of the alloy
is calculated using the formula
where 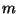 represents each of the three base metals,
represents each of the three base metals,
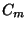 is the thermal constant for metal
is the thermal constant for metal 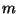 ,
, 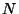 is the set
representing the neighbouring regions,
is the set
representing the neighbouring regions, 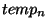 is the temperature of
the neighbouring region,
is the temperature of
the neighbouring region, 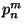 is the percentage of metal
is the percentage of metal 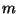 in
neighbour
in
neighbour 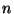 , and
, and 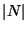 is the number of neighbouring regions.
This computation is repeated until the temperatures converge to
a final value or a reasonable maximum number of iterations is
reached.
is the number of neighbouring regions.
This computation is repeated until the temperatures converge to
a final value or a reasonable maximum number of iterations is
reached.
The values for 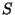 ,
, 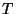 ,
, 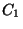 ,
, 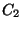 ,
, 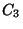 ,
the dimensions of the mesh, and the threshold should be parameters to
the program. Note however, that combinations of these parameters do
not do not converge well. Try values of (0.75, 1.0, 1.25) C1, C2, C3
for your test/demo.
,
the dimensions of the mesh, and the threshold should be parameters to
the program. Note however, that combinations of these parameters do
not do not converge well. Try values of (0.75, 1.0, 1.25) C1, C2, C3
for your test/demo.
Assume that the edges are maximally insulated from their
surroundings.
Your program should graphically display the results by drawing a grid
of points with intensities or colors indicating temperature.
(Alternatively, you can just output them to a file and use something
like gnuplot to display them.)
Acknowledgment: This assignment was adapted from a study by Steve
MacDonald.
B. Reimplement using SIMD parallelism, a GPU, or multiple servers.
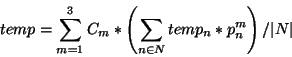
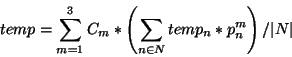
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
the dimensions of the mesh, and the threshold should be parameters to
the program. Note however, that combinations of these parameters do
not do not converge well. Try values of (0.75, 1.0, 1.25) C1, C2, C3
for your test/demo.
,
the dimensions of the mesh, and the threshold should be parameters to
the program. Note however, that combinations of these parameters do
not do not converge well. Try values of (0.75, 1.0, 1.25) C1, C2, C3
for your test/demo.